CS472 - Using GenAI tools in Software Engineering Tasks - Lab
Labs
This individual assignment is due Feb 28th, 2025
Important Note
While this lab may appear lengthy, most of the content is informative and includes illustrations to help you understand the tasks. It is designed to be easy to read and follow.
Lab Structure & Grading
This lab consists of two main tasks:
- Task 1: Quiz (10 points) – A short quiz to assess your understanding on how developers use GenAI to address some software development tasks.
- Task 2: Hands-On Activity (20 points) – A practical exercise where you will apply what you learned.
Introduction to ChatGPT in Software Engineering
In this lab, you’ll learn how to use ChatGPT, a language model developed by OpenAI, to tackle software engineering tasks. ChatGPT can generate human-like text based on input and has become a valuable tool for developers. You’ll explore how developers integrate ChatGPT into their workflow and how to use it responsibly to improve productivity.
This lab builds on research presented at the 2024 International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), where we studied ChatGPT’s role in open-source projects. The insights from this research will help you understand ChatGPT’s impact on software engineering tasks and decision-making.
ChatGPT’s Role in Software Engineering
ChatGPT is widely used across the software development lifecycle, including:
- Requirements engineering – Requirements classification, resolving ambiguity
- Software design – GUI retrieval, rapid prototyping
- Development – Code generation, search, documentation
- Quality assurance – Test generation, bug detection
- Maintenance – Code review, duplicate bug detection
- Management – Effort estimation
For an in-depth discussion, see Section 6 of Hou et al. LLMs for SE: A SLR.
Task 1: Exploring ChatGPT’s Role in Software Engineering
Before moving to hands-on tasks, you’ll first review real-world examples of how developers use ChatGPT in software development.
How Developers Use ChatGPT
The following case studies illustrate three key scenarios where ChatGPT was used in GitHub pull requests:
- Patch Applied (PA) – Code was directly integrated.
- Patch Not Applied (PN) – Suggestions were modified or rejected.
- None Existing Patch (NE) – ChatGPT provided guidance without direct code suggestions.
Key themes include:
- PN Themes: Project adaptation, methodological guidance, specific functionality, technical limitations, and clarifications.
- NE Themes: Conceptual guidance, documentation improvement, education, debugging, and optimization strategies.
Each case includes GitHub pull requests and developer interactions to show ChatGPT’s impact.
Your Task (10 points)
- Read the Case Studies carefully to understand how ChatGPT influenced decisions.
- Take the WebCampus Quiz (10 multiple-choice questions) to check your understanding before proceeding to hands-on exercises.
Case Studies
Patch Applied (PA)
In our lab research, we observe that developers integrate ChatGPT-generated patches at different levels based on project constraints such as maintainability, readability, and coding standards. Our findings indicate that a median integration rate of 25% suggests that most AI-generated patches are only partially adopted, rather than fully applied.
Boxplot of ChatGPT Patch Integration
The figure below illustrates the distribution of ChatGPT-generated code integrated into pull requests. A boxplot analysis of merged pull requests shows three categories of integration:
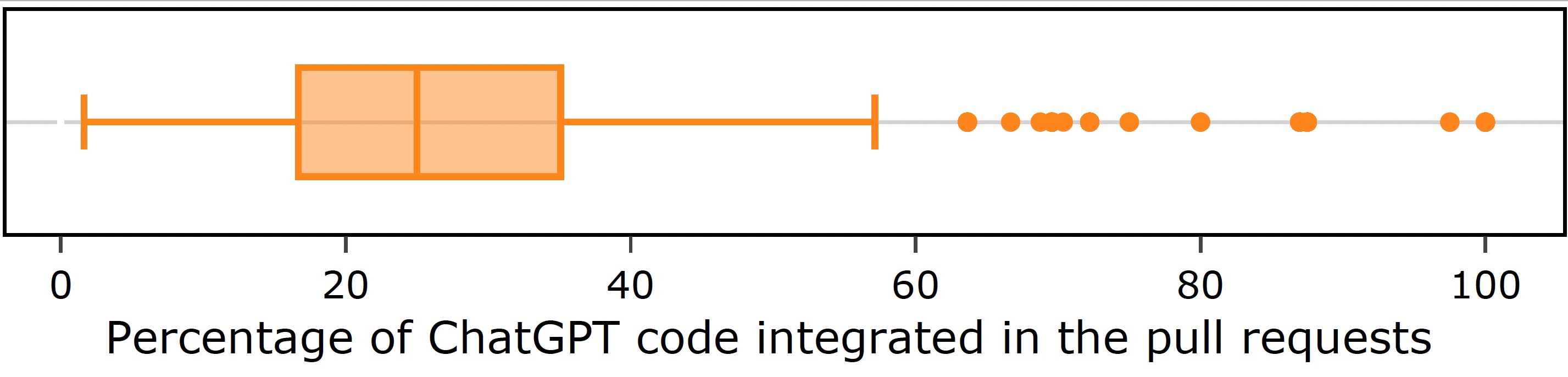
- Low (0–25%) – Only minor elements were used, with significant modifications.
- Moderate (25–75%) – Some parts were integrated, but developers refined the patch to fit project needs.
- High (75–100%) – The AI-generated patch was largely accepted with minimal changes.
This data highlights that ChatGPT serves as a starting point, but developers still refine AI-suggested code before merging it into real-world projects.
Now that we understand the varying levels of ChatGPT patch integration, let’s look at real-world examples where AI-generated patches were applied in GitHub pull requests.
Example 1: Code Duplication and Refactoring
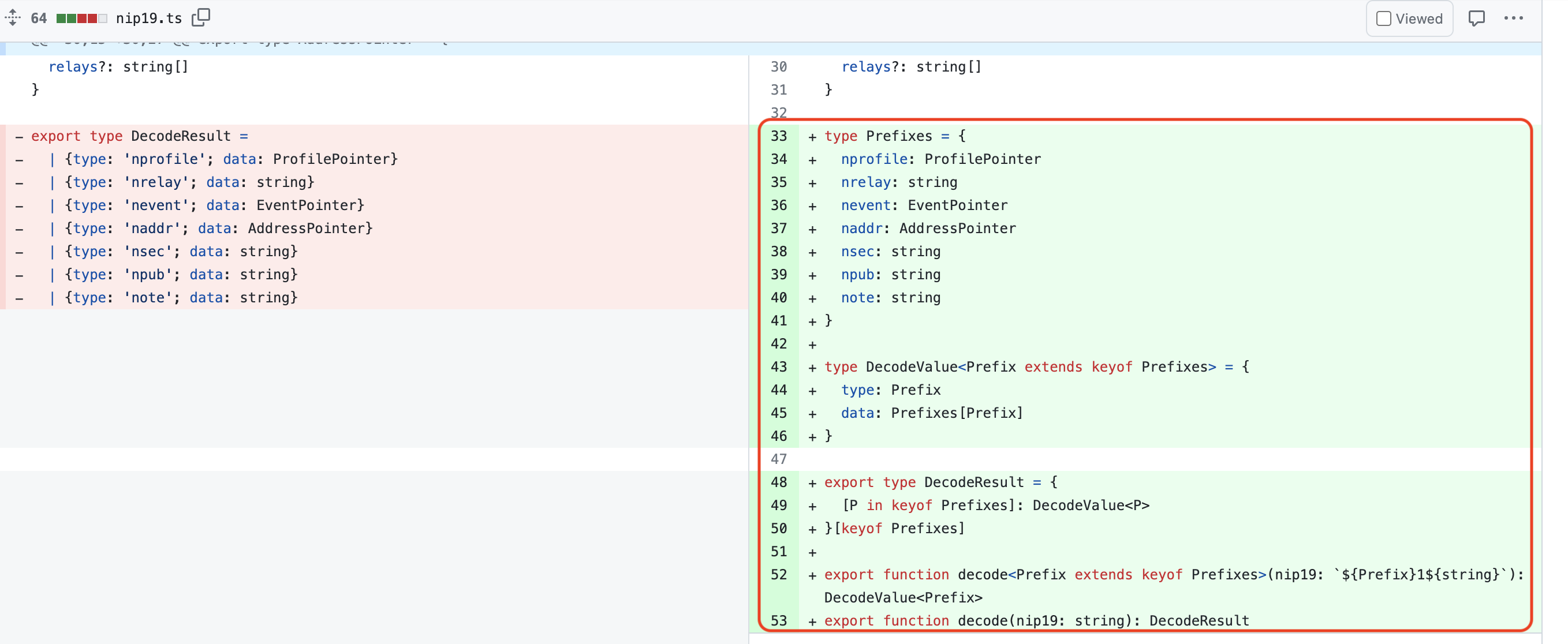
A developer used ChatGPT during the Software maintenance task of code duplication and refactoring in the nostr-tools project. The developer aimed to resolve code repetition and refactor the code.
The pull request shows code changes to address duplication issues, improving code quality. Code duplication often leads to maintenance challenges, bugs, and reduced readability. By using ChatGPT, the developer sought guidance to efficiently refactor the code.
Developer Prompt:
I have some duplication in my TypeScript code. I want to resolve it by creating a discriminated union based on the keys and values of the interface. Is this possible?
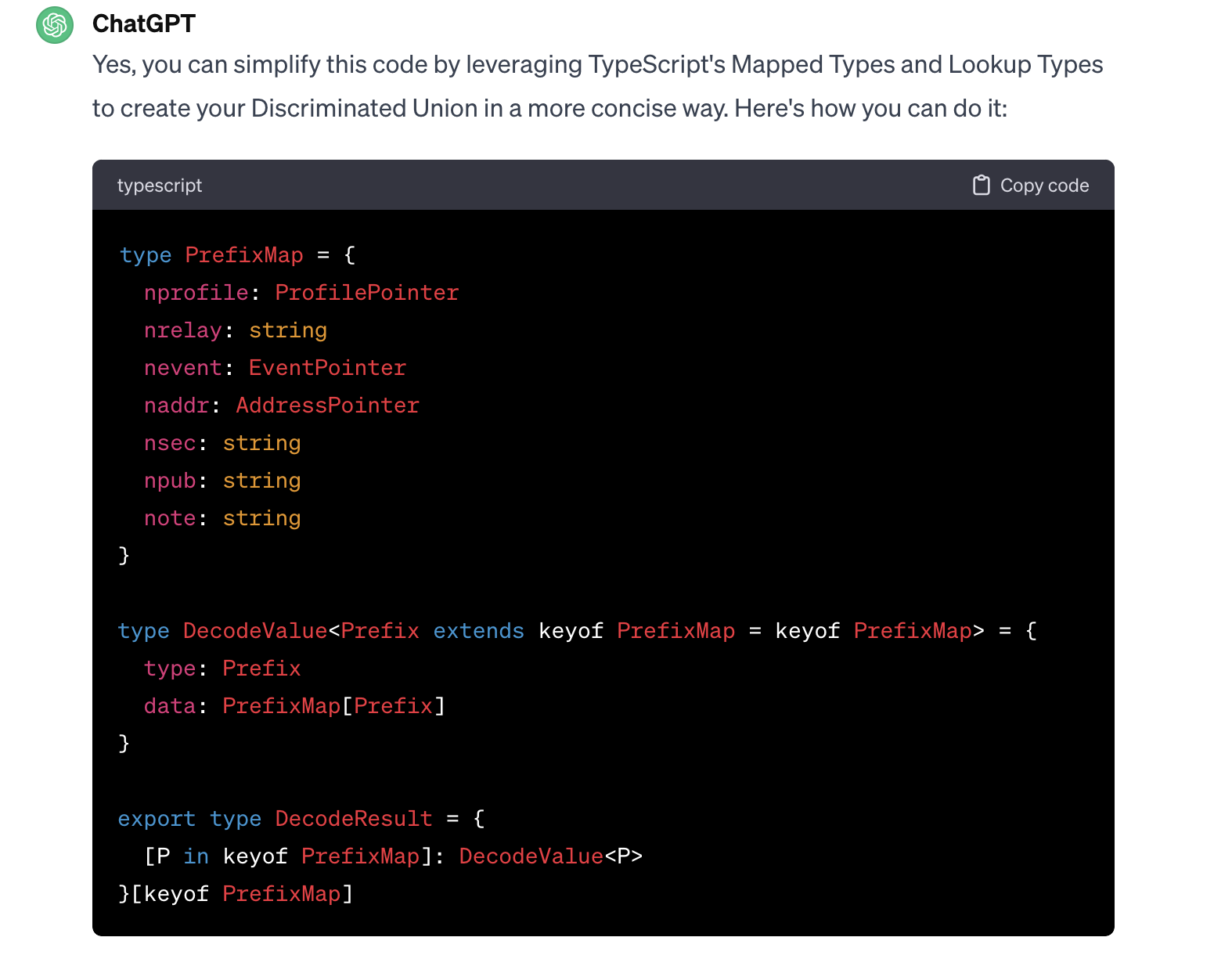
GitHub file diff: View here
Example 2: Deployment Documentation
Links to PR and ChatGPT conversation:
- PR Link
- Note: The original ChatGPT conversation link has been deleted by the developer. However, all the necessary details and context from the conversation are provided here for your reference. You can still follow along with the example using the information already included.
Documentation plays a key role in ensuring effective communication and collaboration in software development. It can take various forms such as:
- Requirements Documentation: Specifications (functional & non-functional).
- Design Documentation: System architecture, data flow.
- Technical Documentation: Code, APIs, algorithms, and data.
- Testing & QA Documentation: Test plans and quality assurance.
- Deployment Documentation: Guidelines for software deployment.
In this case, the developer used ChatGPT to generate user-friendly, concise deployment documentation for the release.sh script.
Developer’s prompt:
Act as a developer advocate with 5 years of experience. Write quick documentation for this `release.sh` script. Use bullet points and short sentences. Add emojis where needed.

As a result, the CONTRIBUTION.md file was updated with documentation from ChatGPT to help new contributors get started.

Example 3: Configuring GitHub Actions Workflow
In Examples 1 and 2 above, the developer used the code generated by ChatGPT “as-is.” However, this example demonstrates another use case where the developer integrates only a portion of the code snippet suggested by ChatGPT. The prompt provided by the developer aligns with the Configuring GitHub Actions Workflow task, which falls under the Software Configuration Management (SCM) activity. SCM encompasses version control, configuration management, and process management. Configuring GitHub Actions workflow specifically relates to automating the building, testing, and deploying of code changes, which aligns with CI practices.
In this case, after reviewing the GitHub link and ChatGPT conversation, we can see that the developer is seeking guidance on setting up and configuring GitHub Actions workflows for the Faker.js library. The GitHub link shows changes made to the GitHub Actions workflow configuration file.
Developer Prompt 1:
Write a GitHub Action yml file that blocks the PR from merging when there is a label named "do NOT merge yet" or "s: on hold"
Developer Prompt 2:
How can I check "s: on hold" with "contains" using "github.event.pull_request.labels.*.name"
Below is the final code snippet generated by ChatGPT and the portion integrated into the GitHub pull request.
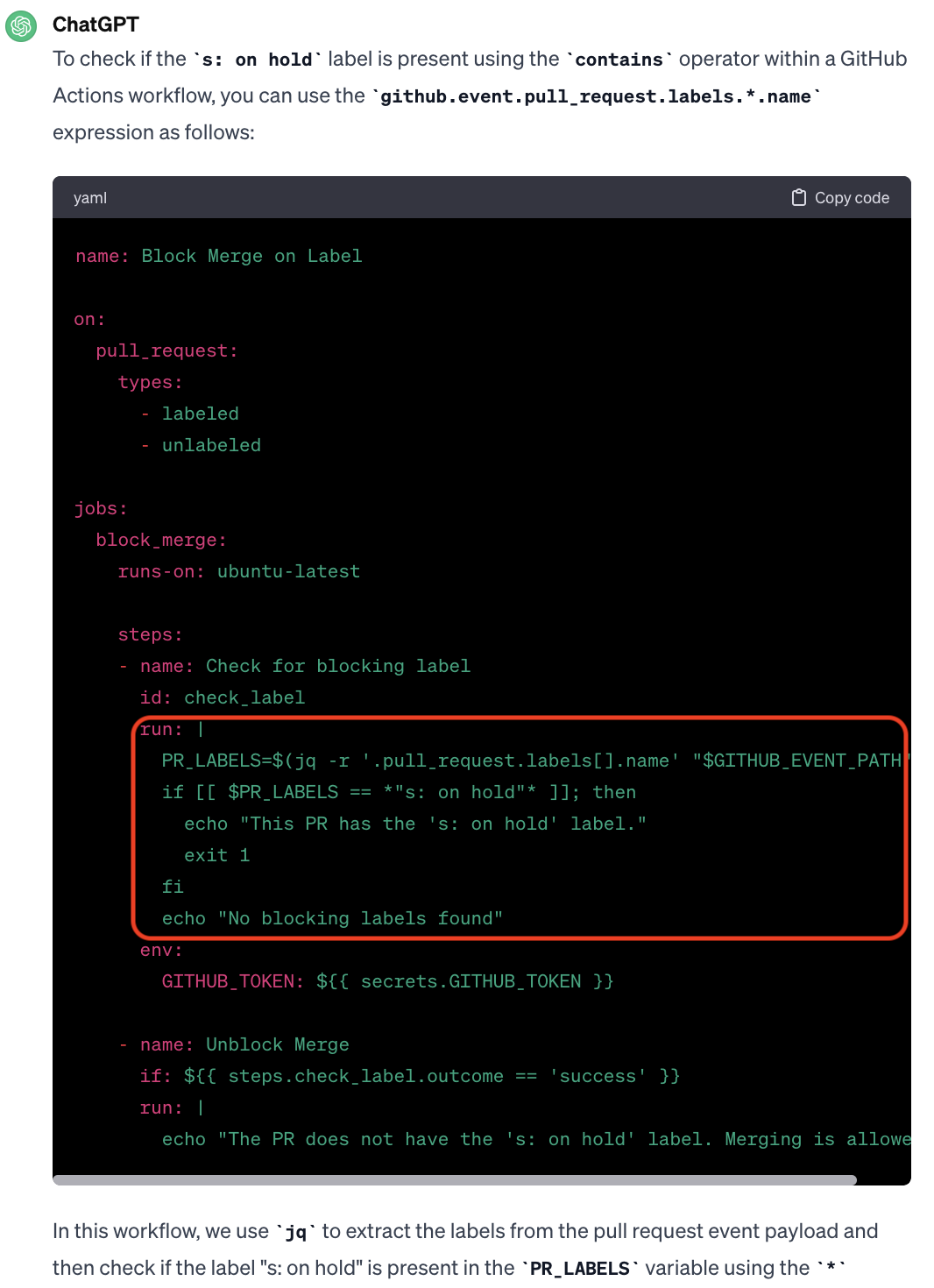
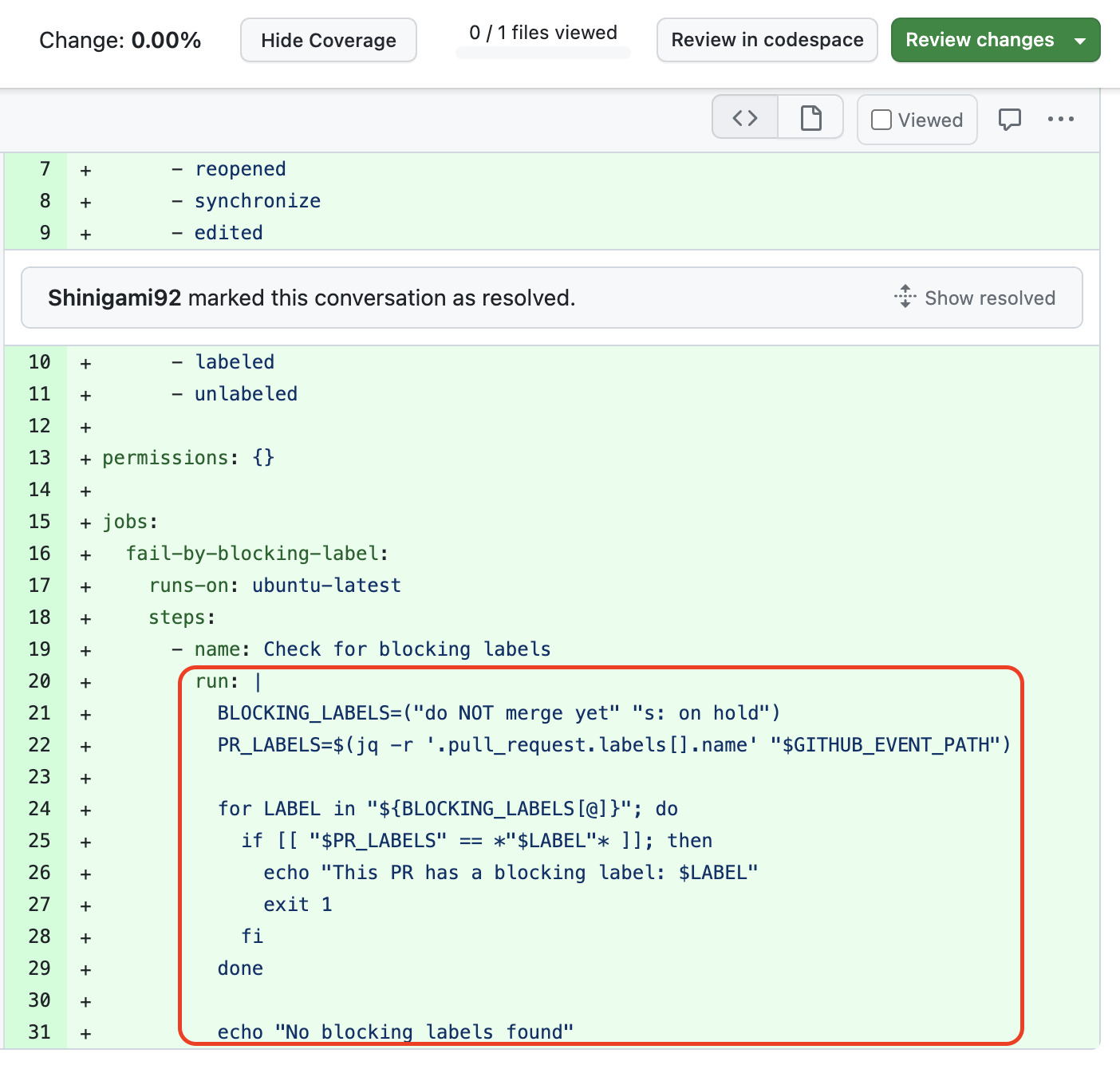
Patch Not Applied (PN)
Example 1: Adaptation and Tailored Solutions
This example shows how ChatGPT’s conceptual advice was adapted for customized solutions to fit unique project needs.
Conversation Summary
- Initial ChatGPT Suggestion: ChatGPT provided a regex for ULID:
^[0-9A-HJKMNP-TV-Z]{26}$to match a 26-character string using base32 encoding. -
Reviewer’s Suggestion: The reviewer (
@lindyhopchris) recommended using Laravel’swhereUlid()regex for consistency, aligning with how ULIDs are handled in the Laravel framework. The Laravel regex provided by the reviewer is[0-7][0-9a-hjkmnp-tv-zA-HJKMNP-TV-Z]{25}This regex specifies that the first character is a digit between 0-7, followed by 25 base32 characters.
-
PR Author’s Acceptance: The author (@Ashk2a) acknowledged the feedback and updated the code (File MatchedIDs.php) to reflect the Laravel-style regex:
public function ulid(): self { return $this->matchAs('[0-7][0-9a-hjkmnp-tv-zA-HJKMNP-TV-Z]{25}'); }
Conclusion
This pull request demonstrates how the developer adapted ChatGPT’s suggested regex to meet the specific requirements of the project. The task falls under the Software Engineering activity of code customization, as the developer further modified the generated code to align with project standards and feedback. This aligns with the theme of adaptation to project needs, where conceptual advice from ChatGPT was tailored to ensure consistency with Laravel’s framework.
Example 2: Methodological Guidance
This theme focuses on how ChatGPT’s advice informs approaches or refined solutions, rather than being directly applied as patches. The emphasis is on broader strategies influenced by ChatGPT.
The developer’s interaction with ChatGPT in this pull request demonstrates a progression from a complex to a simpler, more efficient solution. Here’s a breakdown:
Initial Code (Before ChatGPT’s Suggestion)
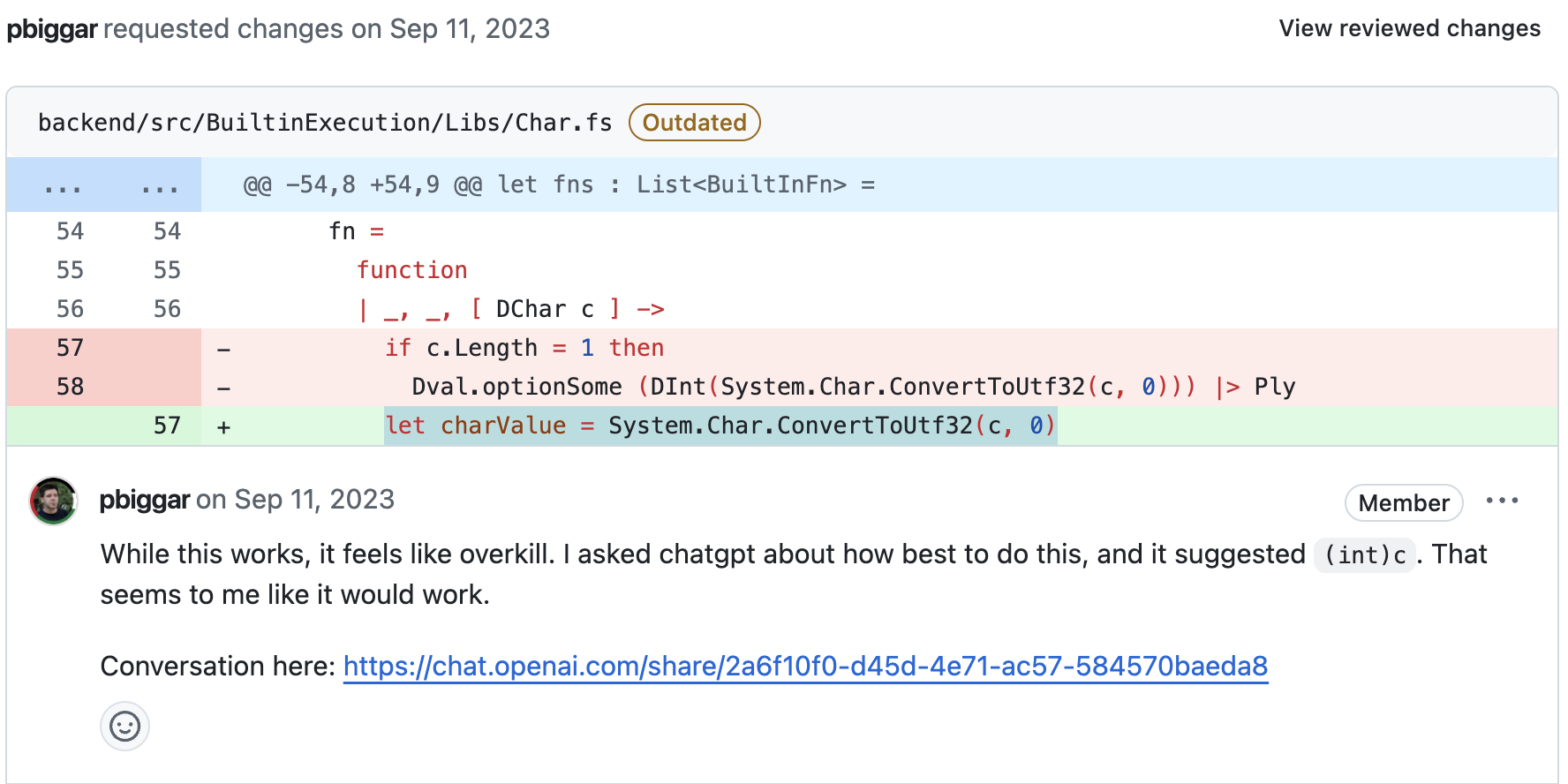
In the initial code, the developer uses System.Char.ConvertToUtf32 to convert a char to its Unicode (UTF-32) code point. While effective, this method is mainly suited for handling UTF-16 surrogate pairs and is unnecessary for basic char values. It’s an overly complex solution for ASCII or basic Unicode characters.
The reviewer (@pbiggar), after consulting ChatGPT, noted that casting the char to an int would achieve the same result in a simpler and more efficient way. ChatGPT suggested casting char to int, which directly returns the Unicode (or ASCII) code point for the character—perfect for most simple characters.
Refined Code (After ChatGPT’s Suggestion)
The refined code can be found in the file backend/src/BuiltinExecution/Libs/Char.fs.
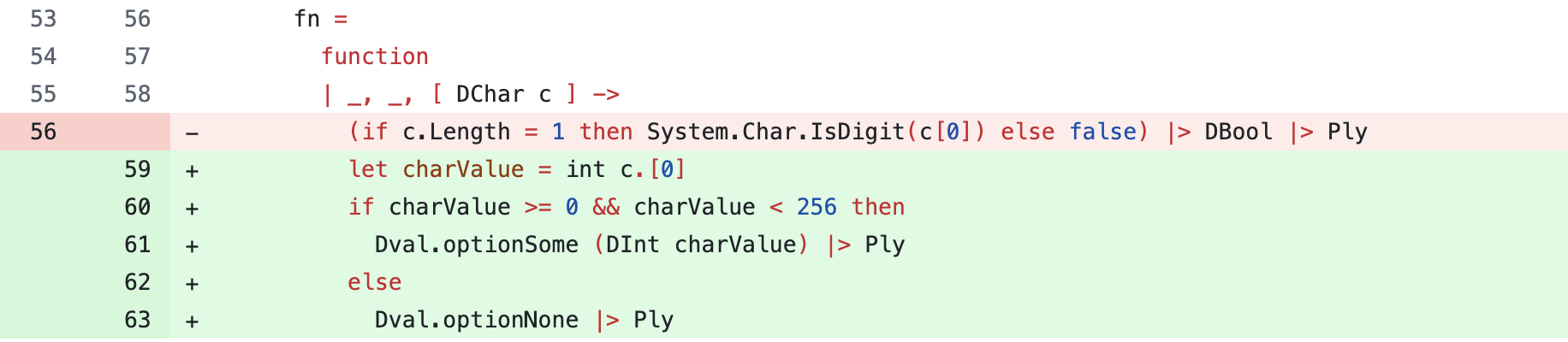
In the updated version:
- Simplified Conversion: The developer replaced
System.Char.ConvertToUtf32withint c.[0], which is a simpler and direct way to get the integer (ASCII/Unicode) value of a character. - Added Validation: Additional logic was included to handle edge cases:
- Digit Check: The code checks if the character is a digit using
System.Char.IsDigit(c[0]). - Range Validation: It verifies that
charValueis within the[0, 256)range, ensuring the value is within the ASCII range. - Conditional Handling: If
charValueis valid, it returnsDval.optionSome (DInt charValue), otherwise it returnsDval.optionNone.
- Digit Check: The code checks if the character is a digit using
Conclusion
The interaction in this pull request is a clear example of methodological guidance, where ChatGPT’s advice helps refine the developer’s approach instead of being directly applied as a patch. This refinement aligns with the Software Engineering task of program repair, as it involved simplifying and improving the initial code to address inefficiencies.
By following ChatGPT’s advice, the developer made the code more efficient and easier to maintain, demonstrating how methodological guidance can lead to better solutions in software engineering.
None Existing Patch (NE)
Example 1: Conceptual Guidance & Theoretical Advice
This theme emphasizes programming concepts, design principles, and optimization strategies, focusing on best practices for readability and maintainability without specific code implementations.
Let’s break down the situation to understand how the developer changed their code based on the ChatGPT conversation:
Original Problem
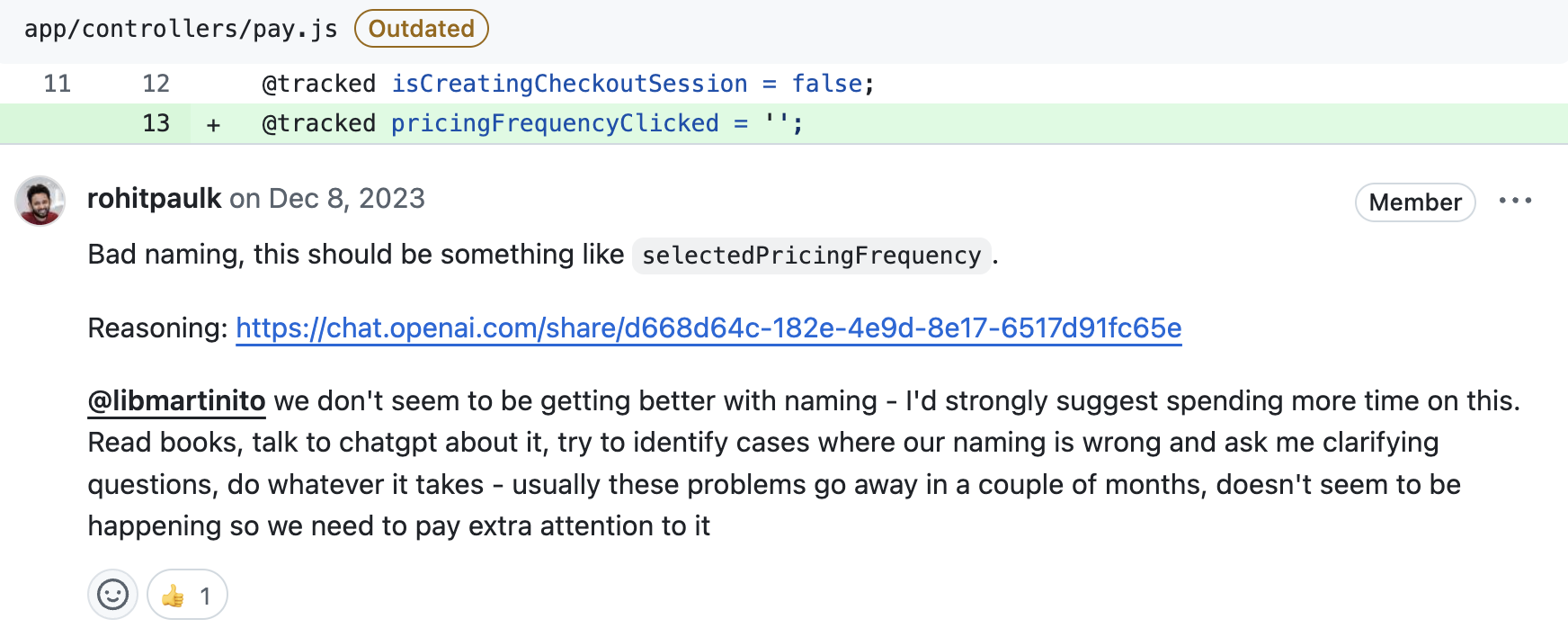
The developer was using the variable name pricingFrequencyClicked, which was problematic because the name implied an action (a click) rather than a state (the selected frequency). This didn’t accurately reflect what the variable was being used for: to store the selected pricing frequency (e.g., ‘monthly’ or ‘yearly’).
Developer’s Implementation
The final updates in the PR can be viewed in the file: app/controllers/pay.js.

After the ChatGPT conversation, the developer renamed pricingFrequencyClicked to selectedPricingFrequency. This new name more accurately reflects that the variable holds the user’s selection for pricing frequency, improving both readability and maintainability of the code.
ChatGPT’s Advice
ChatGPT highlighted the issue with the variable name, explaining that pricingFrequencyClicked was not appropriate because it didn’t align with the variable’s purpose. It suggested using a name like selectedPricingFrequency to more accurately reflect that the variable holds a selection, not an action.
Conclusion
This interaction falls under the “Conceptual Guidance & Theoretical Advice” theme, where ChatGPT’s recommendations helped improve the clarity and maintainability of the code by suggesting better naming conventions. This aligns with the software engineering tasks of code review and code quality enhancement, as it involved refining naming practices to enhance readability and maintainability.
In this case, ChatGPT played a key role in informing the process of improving code structure and long-term maintainability, aligning with these software engineering tasks.
Example 2: Debugging and Optimization Strategies
This theme focuses on debugging methods, performance optimization, and refining algorithms, offering strategic insights into problem-solving approaches without providing specific code snippets.
Let’s break down how the developer improved their code based on a conversation with ChatGPT:
Original Code
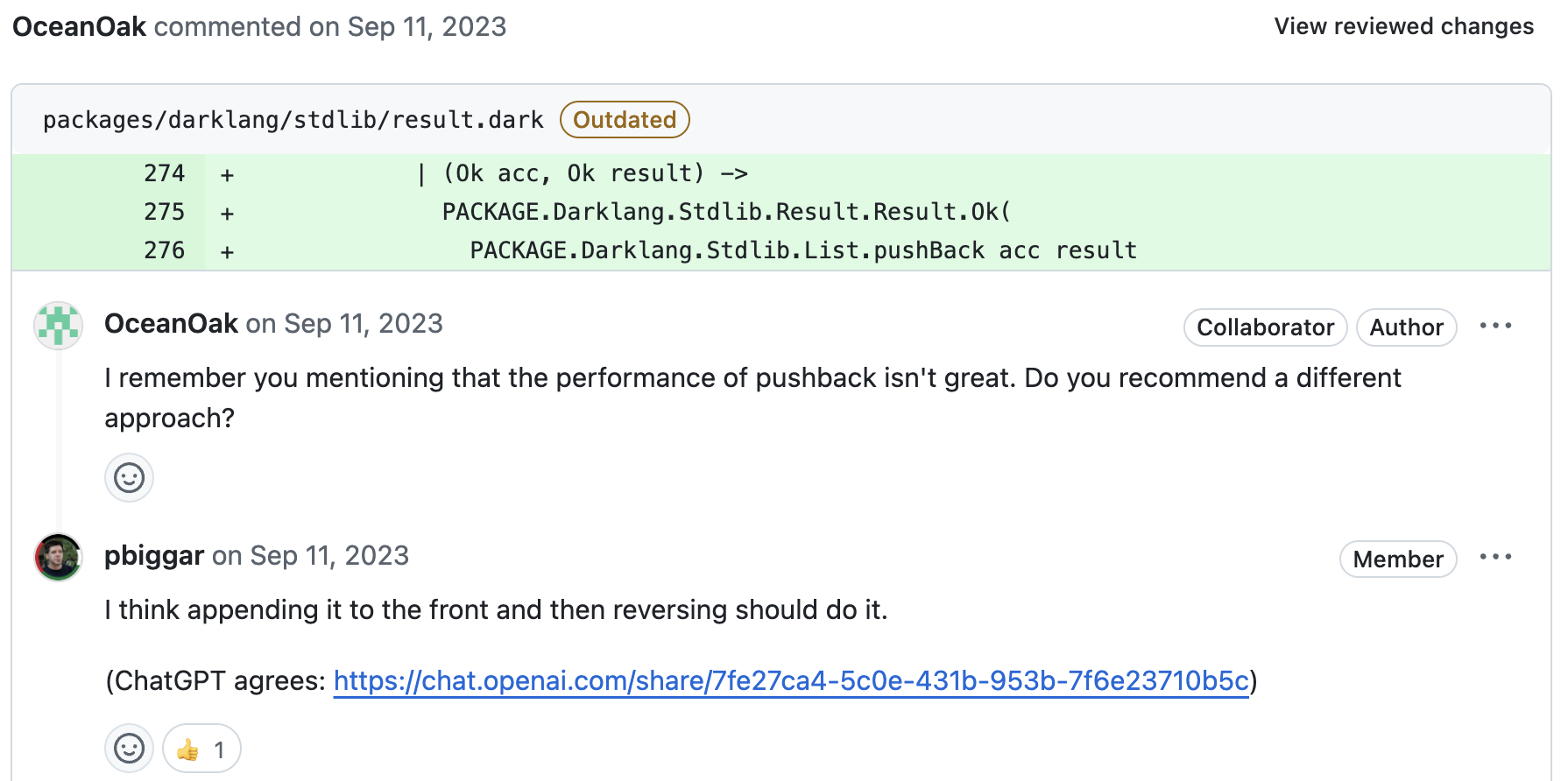
Initially, the developer was using pushBack, which appends an element to the end of a list. However, repeatedly using this operation can be inefficient, as it may require traversing the entire list, especially in larger datasets.
ChatGPT’s Advice
After consulting ChatGPT, the developer received a suggestion to optimize the list operation by switching to push (which likely adds elements to the front of the list) and then reversing the list at the end. This approach is generally more efficient because adding to the front of the list is an O(1) operation in many functional languages, whereas pushBack can be an O(n) operation, where n is the length of the list.
Updated Code
The optimized code can be found in this PR file: backend/testfiles/execution/stdlib/result.dark.
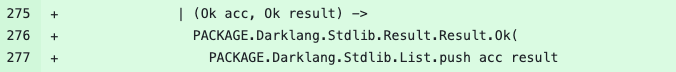
In this updated code:
- The developer switched to using
push(adding to the front) and planned to reverse the list at the end. - This new approach enhances performance, as adding to the front of the list is typically O(1), whereas using
pushBackcould result in O(n) complexity.
Conclusion
This interaction falls under the Debugging & Optimization Strategies theme, where ChatGPT provided advice to improve performance. Rather than directly offering a code solution, ChatGPT suggested a strategy—appending elements to the front of the list and reversing it later—to optimize performance. This aligns with the Software Engineering task of performance optimization, where the developer refined the algorithm based on ChatGPT’s advice, ultimately enhancing the efficiency of the code.
ChatGPT played a key role in guiding the developer toward a more efficient solution for handling list operations, demonstrating how strategic advice can lead to performance improvements in software engineering.
Getting Started With ChatGPT
To start using ChatGPT, go to https://chat.openai.com/ and create a free account. For this class, the free version of ChatGPT 3.5 is sufficient.
To make the most of ChatGPT, it’s important to provide well-structured prompts. The concept of Prompt Engineering is explored in this research paper: A Prompt Pattern Catalog to Enhance Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT.
Sharing Your ChatGPT Conversations on GitHub
Sharing your ChatGPT conversations with other developers can be highly beneficial for several reasons, such as:
- Collaborative problem-solving
- Learning and knowledge sharing
- Code review and improvement
- Gaining diverse perspectives
- Sharing best practices and tips
- Avoiding common pitfalls
- Building a supportive community
- Ethical considerations
- Innovation and exploration
How to Share Your ChatGPT Conversations
-
Generating a Shareable Link: Once you’re ready to share your ChatGPT conversation, follow the steps below to generate a shareable link. Note: Your personal profile will be anonymized when the conversation link is generated.
-
Sharing on GitHub: After copying the link, you can include it in various places on GitHub, such as a pull request (PR), issue, or commit message. For instance, if ChatGPT helped you solve a bug, you could include the link in the PR description or during a PR review. See examples below:
-
Adding the conversation link in a PR description:
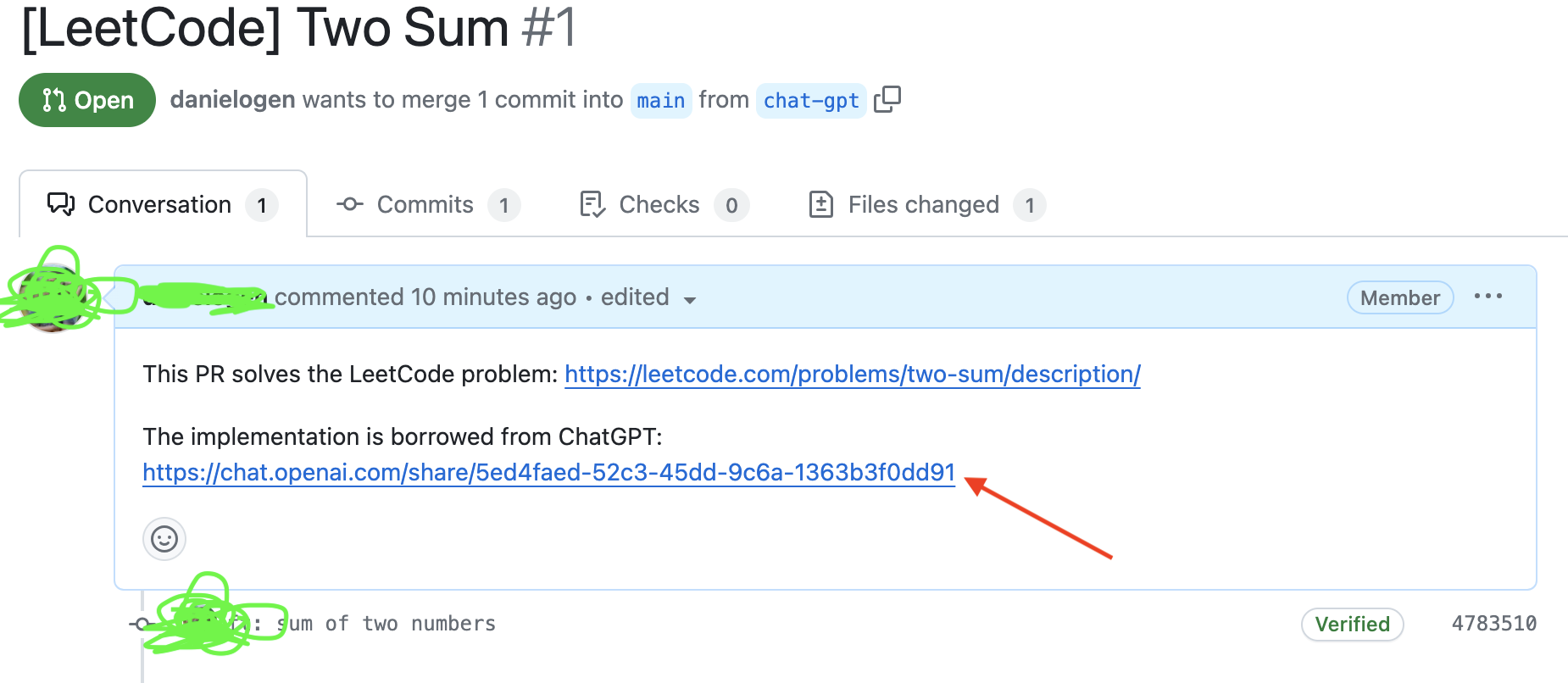
-
Adding the conversation link during PR review:
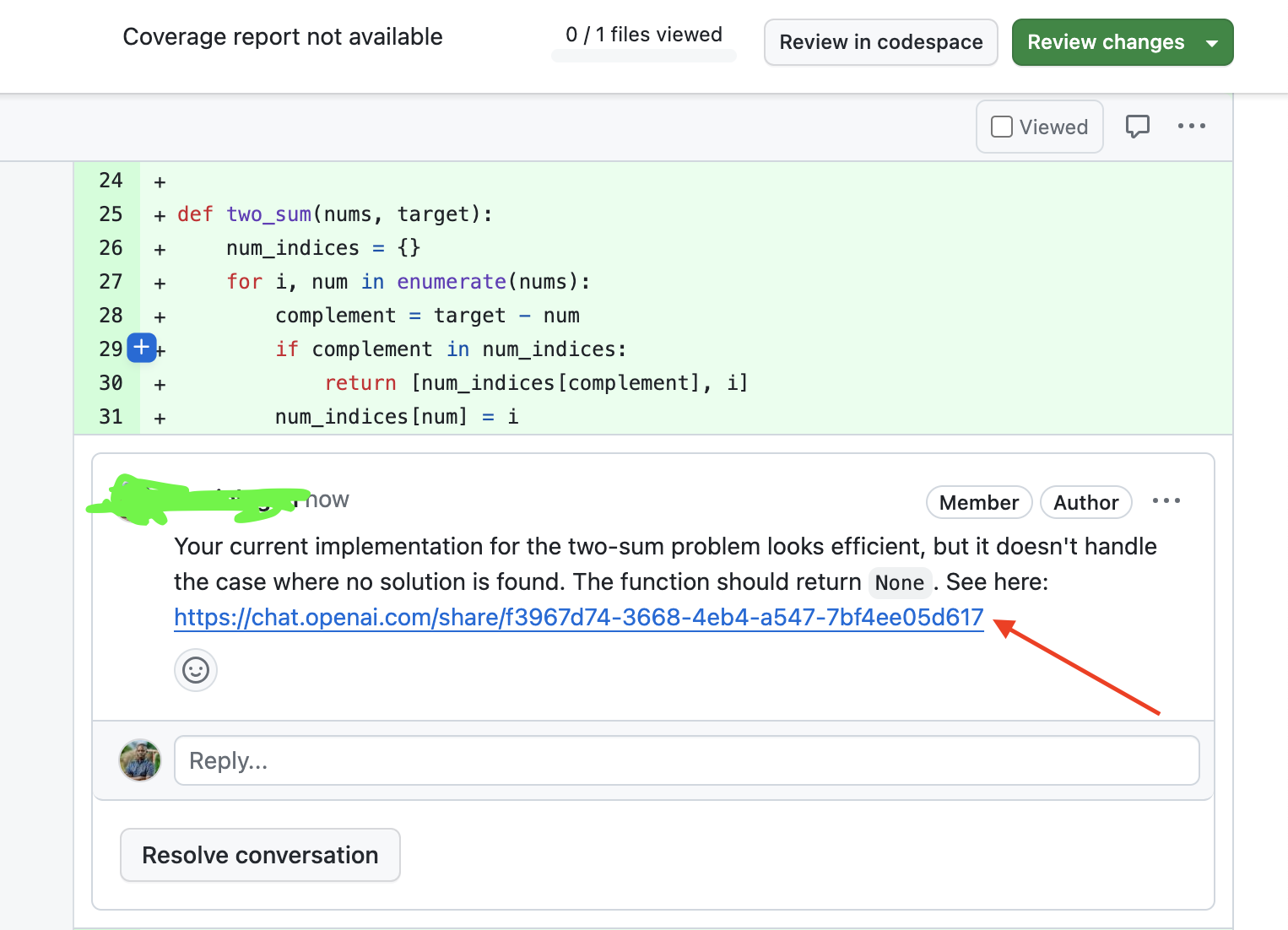
-
Task 2: Hands-on with ChatGPT (20 points)
In Task 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3, you will work on your team repository, where previous lab tasks were submitted. You’ll use ChatGPT to improve code quality, documentation, and comprehension.
- The author must use ChatGPT during the development process.
- Your goal is to enhance your code by applying ChatGPT’s suggestions while ensuring correctness and maintainability.
Organizational Guidelines:
- Repository Structure:
- To maintain consistency, store your files inside the
gen_aidirectory, with subfolders for each task. For example:gen_ai/task2.1/yourname_refactor_code.py gen_ai/task2.2/yourname_docstring_update.py - Check if the directories already exist before creating them. If another team member has already added them and merged their pull request, pull the latest changes instead of recreating them (see instructions below).
- To maintain consistency, store your files inside the
- Pull Requests (PRs):
- Open a PR for each task with clear descriptions, referencing ChatGPT suggestions.
- Example PR Title:
“Refactored function X using ChatGPT’s recommendation.”
- PR Description Example:
“Refactored the loop structure to improve efficiency. Suggested by ChatGPT [conversation link].”
Verification and Collaboration:
-
Ensuring Your Local Repository is Up-to-Date:
Before making any modifications, ensure you have the latest version of the repository by running:git checkout main git fetch upstream # Fetch the latest changes from the team repository (`upstream/main`) without merging yet. git merge upstream/main # Merge the latest changes from the team repository into your local main branch. git push origin main # Push the updated main branch to your fork.
Task 2.1: Code Refactoring Using ChatGPT
Objective: Refactor a code snippet using ChatGPT to improve code quality and readability.
Instructions:
- Select a Code Snippet: Choose a code snippet from your current project, an open-source repository, or a past assignment from your previous programming classes. Open an issue on the team repository identifying specific problems (e.g., duplication, inefficiency, poor readability).
- Consult ChatGPT: Ask ChatGPT for advice on how to refactor the code. Provide context on the code’s purpose and areas needing improvement. Copy the link to the ChatGPT conversation.
- Open a Pull Request (PR): Submit a PR with the selected code snippet. Reference the issue created earlier (e.g., “Closes #123”) and provide a summary of the refactoring goal in the PR description.
- Implement Refactorings: Apply ChatGPT’s suggestions to improve the code’s quality and readability. Ensure that the functionality of the code remains intact after refactoring.
- Merge PR: Once your colleague has reviewed the PR and confirmed the improvements, you can merge the PR into the team repository.
Task 2.2: Improving Documentation with ChatGPT
Objective: Use ChatGPT to enhance documentation for a selected code snippet.
Instructions:
- Select a Code Snippet: Choose a code snippet from your current project, an open-source repository, or a past assignment from your previous programming classes that lacks proper documentation. Open an issue on the team repository to take ownership of the task.
- Consult ChatGPT: Ask ChatGPT to help generate clear and user-friendly documentation for the code. Provide relevant context about the code’s functionality and any areas where the documentation is lacking.
- Open a Pull Request (PR): Submit a PR with the improved documentation to your team repository. Reference the issue using keywords like “Closes #123” or “Fixes #123.”
- Update Documentation: Based on ChatGPT’s suggestions, improve the code documentation to ensure it is clear, complete, and easy to understand.
- Merge PR: After the review is completed and improvements are confirmed, merge the PR into the main branch of your team repository.
Task 2.3: Understanding Complex Code with ChatGPT
Objective: Use ChatGPT to help comprehend and improve a complex code segment.
Instructions:
- Select a Complex Code Segment: Choose a complex code segment from your current projects, an open-source repository, or a past programming assignment. Open an issue on your team repository detailing the complexity and the challenges you’re facing in understanding the code.
- Consult ChatGPT: Provide ChatGPT with the code and highlight specific areas where you need clarity or improvements. Ask for suggestions on how to simplify, optimize, or improve the code.
- Open a Pull Request (PR): Submit a PR to your team repository with the selected code segment. Reference the issue you created and explain the goal of simplifying or optimizing the code in the PR description.
- Implement Changes: Apply ChatGPT’s recommendations to simplify or optimize the code, ensuring that functionality is maintained.
- Merge PR: Once the review is complete and all changes are confirmed, merge the PR into the team repository.
Task 3: Summary Report
Write a brief report that includes:
Task Summary:
- For each task (Exploring ChatGPT’s Role in Software Engineering, Code Refactoring, Documentation Assistance, Understanding Complex Code), provide a short description (1-2 sentences) of what you did.
- Include the link to the individual pull request (PR) for each task.
Submission:
- Submit your report on Web Campus.